Methods
Characterization of Upwelling and Downwelling Phases
The process of characterization of the upwelling index (UI) phases is schematized in the figure 1. Initialy we remove the seasonal cycle of the spatial series of the environmental variables. Due to the upwelling index has a seasonal component if we do not remove the effect of this temporal factor, the analysis was characterizing exclusively the environmental conditions of the winter and summer seasons.
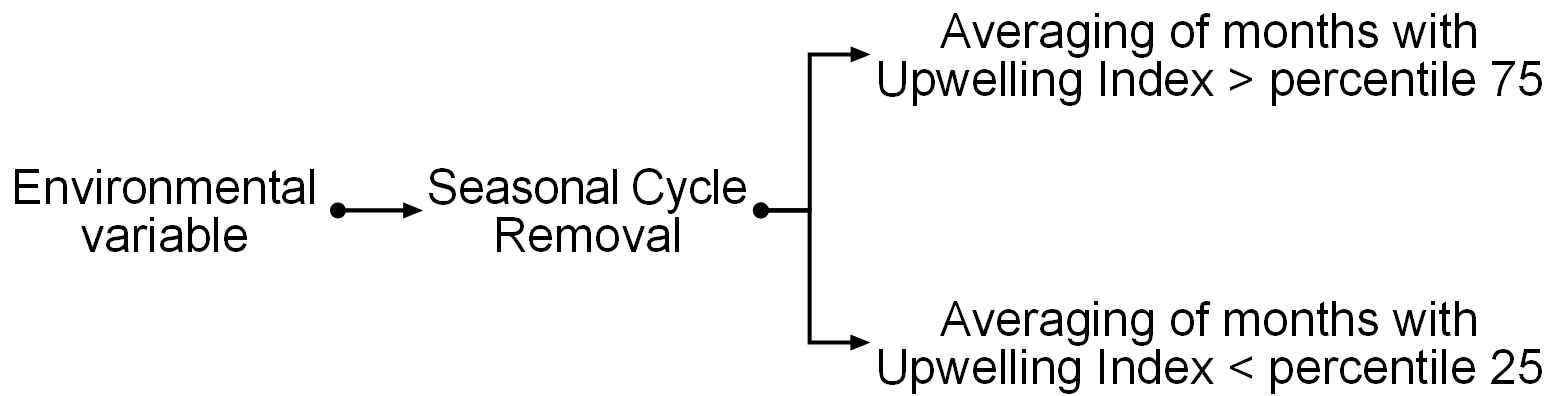
After the preprocessing of the environmental variables we define the months of the upwelling (downwelling) phase those that has upwelling index values higher than percentile 75 of the UI serie (lower than percentile 25 of the UI serie).
In order to define the characteristics of the UI phases, the enviromental variables were averaged following the month classification of the previous data processing step.
Upwelling index calculation
Instituto Español Oceanografía coastal upwelling indices are calculated based upon Ekman's theory of mass transport due to wind stress and are available in our website (www.indicedeafloramiento.ieo.es). The methodology used was the proposed by Bakun 1993 as indicated in the technical reports published by the IEO.
The basic input data to calculate UI is the sea level pressure field over the ocean. The Navy Operational Global Atmospheric Prediction System (NOGAPS) model 6 hourly sea level pressure (SLP, hPa) database, maintained by FNMOC (Fleet Numerical Meteorology and Oceanography Center, US Navy’s), is used to calculate UI following Lavin 1991.
FNMOC produces operational forecasts of the state of the atmosphere and the ocean several times daily and maintains archives of several important parameters. These parameters are model derived products which are routinely distributed to researchers. Additional information can be obtained from the Pacific Fisheries Environmental Laboratory (PFEL) (www.pfel.noaa.gov)
The meridional (v) and zonal (u) winds components of the position 43ºN 11ºW are calculated using the following equations:
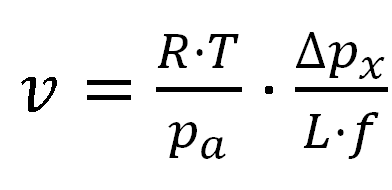
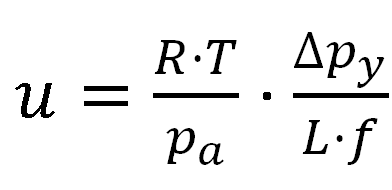
where R is the ideal gas constant (R = 258 j·Kg-1K-1), T is the standard atmosphere temperature (T = 288 K), pa is standard atmospheric pressure (pa = 1013.5 hPa), Dpx and Dpy are the zonal and meridional pressure difference (hPa), L (km) the distance between the locations used to calculate pressure gradient and f is the Coriolis parameter defined as twice the vertical component of the Earth’s angular velocity (Ω) about the local vertical or ƒ = 2Ωsin (θ) at latitude θ.
Ekman transport (Q, m3·s-1·km-1) was calculated using the components of wind speed at 10 m above sea level (u and v), seawater density (ρw = 1025 kg m-3), a dimensionless empirical drag coefficient (Cd = 1.4 × 10-3), and air density (ρa = 1.22 kg m-3, normal conditions) by means of:
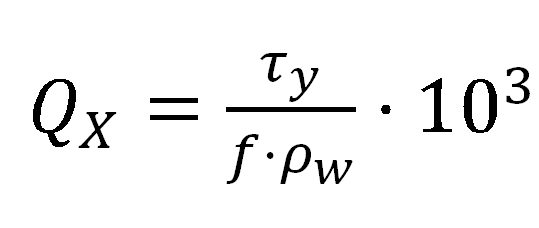
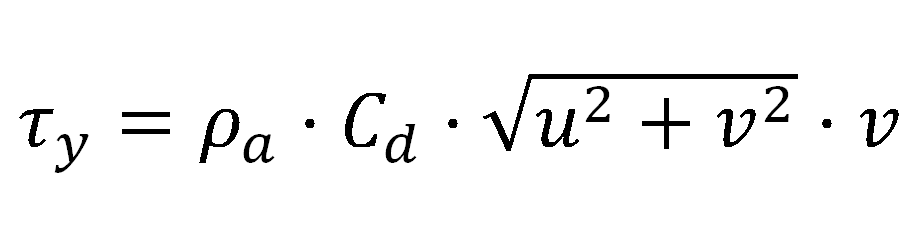
where, the x subscript corresponds to the zonal component and the y subscript to the meridional one. Discretization effects were smoothed by calculating Ekman transport values at each point as the average of its nearest neighbours.
Finally UI is defined as -Qx (m3 s-1 km-1) that is the volume transport per distance unit of an alongshore section. The sign of Ekman transport is changed to define positive (negative) values of UI as response of upwelling (downwelling) favourable winds.
Environmental Varibles
In order to characterize the UI phases, we used different environmental variables databases. The information of each variable are showed in table 1